Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sr in highly radioactive aqueous samples via conversion to a kinetically stable 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid complex followed by concentration-separation-fractionation based on capillary electrophoresis-liquid scintillation
Sr in highly radioactive aqueous samples via conversion to a kinetically stable 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid complex followed by concentration-separation-fractionation based on capillary electrophoresis-liquid scintillationOuchi, Kazuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Hirose, Kazuki*; Kurosawa, Yuika*; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Shibukawa, Masami*; Saito, Shingo*
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1298, p.342399_1 - 342399_7, 2024/04
Given that conventional methods of high-dose sample analysis pose substantial exposure risks and generate large amounts of secondary radioactive waste, faster procedures allowing for decreased radiation emission are highly desirable. To address this need, we developed a  Sr
Sr quantitation technique that is based on liquid scintillation counting-coupled capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) with two-point detection and relies on the rapid concentration, separation, and fractionation of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-complexed
quantitation technique that is based on liquid scintillation counting-coupled capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) with two-point detection and relies on the rapid concentration, separation, and fractionation of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-complexed  Sr
Sr in a single run. This method, which allows for the handling of high-dose radioactive specimens at the microliter level and is substantially faster than conventional ion-exchange protocols, was used to selectively quantify
in a single run. This method, which allows for the handling of high-dose radioactive specimens at the microliter level and is substantially faster than conventional ion-exchange protocols, was used to selectively quantify  Sr
Sr in real high-dose waste. The successful concentration-separation in ctITP was ascribed to the inertness of the Sr-DOTA complex to dissociation.
in real high-dose waste. The successful concentration-separation in ctITP was ascribed to the inertness of the Sr-DOTA complex to dissociation.
Yamashita, Kiyoto; Maki, Shota; Yokosuka, Kazuhiro; Fukui, Masahiro; Iemura, Keisuke
JAEA-Technology 2023-023, 97 Pages, 2024/03
The incinerator adopted to incineration room, Plutonium Waste Treatment Facility had been demonstrated since 2002 for developing technologies to reduce the volume of fire-resistant wastes such as vinyl chloride (represented by Polyvinyl chloride bags) and rubber gloves for Radio Isotope among radioactive solid wastes generated by the production of mixed oxide fuels. The incinerator, cooling tower, and processing pipes were replaced with a suspension period from 2018 to 2022, which fireproof materials on the inner wall of the incinerator was cracked and grown caused by hydrogen chloride generated when disposing of fire-resistant wastes. This facility consists of the waste feed process, the incineration process, the waste gas treatment process, and the ash removal process. We replaced the cooling tower in the waste gas treatment process from March 2020 to March 2021, and the incinerator in the incineration process from January 2021 to February 2022. In addition, samples were collected from the incinerator and the cooling tower during the removing and dismantling of the replaced devices, observed by Scanning Electron Microscope and X-ray microanalyzer, and analyzed by X-ray diffraction to investigate the corrosion and deterioration of them. This report describes the method of setting up the green house, the procedure for replacing them, and the results from analysis in corrosion and deterioration of the cooling tower and incinerator.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2023-025, 117 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of extremely small amount analysis technology for fuel debris analysis" conducted in FY2022. Understanding the properties of fuel debris is necessary for handling, criticality control, storage control, etc. A key technique is the chemical analysis of actinide nuclides. We develop sample pretreatment technology and separation / analysis process required for chemical analysis. The purpose of this study is to streamline future planned fuel debris analysis. To promote 1F decommissioning, we will train human resources through on-the-job training.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Fukushima University*
JAEA-Review 2023-024, 109 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of methodology combining chemical analysis technology with informatics technology to understand perspectives property of debris and tie-up style human resource development" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to goal of this study is to implement a research plan relate to a development of combinational technology of new chemical analysis with informatics, and the aim is to develop new system for whole image estimation system using small quantities of information.
Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Kawata, Manabu; Shiomi, Tadahiko; Li, Y.
JAEA-Research 2024-001, 206 Pages, 2024/03
In the assessment of seismic safety and the design of building structures in nuclear facilities, lumped mass models have been used as standard methods. Recent advances in computer capabilities allow the use of three-dimensional finite element (3D FE) models to account for the 3D behavior of buildings, material nonlinearity, and the nonlinear soil-structure interaction effect. While 3D analysis method has many advantages, it is necessary to ensure its reliability as a new approach. The International Atomic Energy Agency performed an international benchmark study using the 3D FE analysis model for reactor building of Unit 7 at TEPCO's Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station based on recordings from the Niigataken Chuetsu-oki Earthquake in 2007. Multiple organizations from different countries participated in this study and the variation in their analytical results was significant, indicating an urgent need to improve the reliability of the analytical results by standardization of the analytical methods using 3D FE models. Additionally, it has been pointed out that it is necessary to understand the 3D behavior in the seismic fragility assessment of buildings and equipment, using realistic seismic response analysis method based on 3D FE models. In view of these considerations, a guideline for the seismic response analysis method using a 3D FE model was developed by incorporating the latest knowledge and findings in this area. The purpose of the guideline is to improve the reliability of the seismic response analysis method using 3D FE model of reactor buildings. The guideline consists of a main body, commentaries, and appendixes. The standard procedures, recommendations, key points to note, and technological bases for conducting seismic response analysis on reactor buildings using 3D FE models are provided in the guideline. In addition, the guideline will be revised reflecting the latest knowledge.
Nagata, Hiroshi; Omori, Takazumi; Maeda, Eita; Otsuka, Kaoru; Nakano, Hiroko; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2023-033, 40 Pages, 2024/01
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) was decided as a one of decommission facilities in April 2017. In order to submit the decommissioning plan to the Nuclear Regulation Authority, the type of accident assumed in the first stage of the decommissioning plan was selected, and the public exposure dose was evaluated. A fuel handling accident and a fire accident during storage of waste were selected as assumed accidents in the first stage of the decommissioning plan. An evaluation of the public exposure dose from the radioactive materials released into the atmosphere due to these accidents was estimated to be a maximum of 0.019 mSv (due to a fire accident during storage of waste). This estimated value was found to be sufficiently smaller than the judging criteria (5 mSv), and not to pose a significant risk of radiation exposure to the general public.
Tamura, Koji; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Karino, Takahiro; Shibata, Takuya; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 8 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)HPC Technology Promotion Office
JAEA-Review 2023-018, 159 Pages, 2023/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) conducts research and development (R&D) in various fields related to nuclear power as a comprehensive institution of nuclear energy R&Ds, and utilizes computational science and technology in many activities. Over the past 10 years or so, the publication of papers utilizing computational science and technology at JAEA has accounted for about 20 percent of the total publications each fiscal year. The supercomputer system of JAEA has become an important infrastructure to support computational science and technology. In FY2022, the system was used for R&D of light water reactors, high-temperature gas reactors, and fast reactors to contribute to carbon neutrality as a priority issue, as well as for JAEA's major projects such as Various R&D related to nuclear science and technology, R&D related to the response to the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Development of technology for treatment and disposal of high-level radioactive waste, Support of nuclear safety regulation and nuclear disaster prevention, and safety research for this purpose. This report presents a great number of R&D results accomplished by using the system in FY2022, as well as user support, operational records and overviews of the system, and so on.
 ,
,  , and X-ray spectrum analysis
, and X-ray spectrum analysisOshima, Masumi*; Goto, Jun*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Asai, Masato; Kin, Tadahiro*; Shinohara, Hirofumi*
Isotope News, (790), p.19 - 23, 2023/12
When analyzing samples that contain many radionuclides at various concentrations, such as radioactive waste or fuel debris, it is difficult to apply general spectrum analysis methods and is necessary to chemically separate each nuclide before quantifying it. The chemical separation is especially essential for analysis using a liquid scintillation counter (LSC). In this report, the authors explain the newly developed spectral determination method (SDM) in which the entire spectrum is fitted to quantify radioactivity of nuclides mixed in a sample. By applying the SDM to  - and X-ray spectrum measured by LSC and
- and X-ray spectrum measured by LSC and  -ray spectrum measured by Ge detector simultaneously, the authors demonstrated that radioactivity of 40 radionuclides mixed in a sample at concentrations varying by two orders could be quantified, which is useful to simplify chemical separation process in radionuclide quantification.
-ray spectrum measured by Ge detector simultaneously, the authors demonstrated that radioactivity of 40 radionuclides mixed in a sample at concentrations varying by two orders could be quantified, which is useful to simplify chemical separation process in radionuclide quantification.
Sato, Ikken; Yoshikawa, Shinji; Yamashita, Takuya; Shimomura, Kenta; Cibula, M.*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 414, p.112574_1 - 112574_20, 2023/12
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(4), p.32_1 - 32_13, 2023/12
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Maeda, Makoto; Komeda, Masao
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1301 - 1312, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology) Nb by activation method and half-life of
Nb by activation method and half-life of  Nb by mass analysis
Nb by mass analysisNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1361 - 1371, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross section (
 ) and resonance integral (I
) and resonance integral (I ) for
) for  Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of
Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of  Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25-
Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25- m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of
m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of 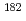 Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by
Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by  -ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the
-ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the 
 and I
and I values were derived as 1.11
values were derived as 1.11 0.04 barn and 10.5
0.04 barn and 10.5 0.6 barn, respectively. After the
0.6 barn, respectively. After the  -ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both
-ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both  -ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of
-ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of  Nb was derived as (2.00
Nb was derived as (2.00 0.15)
0.15) 10
10 years.
years.
Maruyama, Shuhei; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1372 - 1385, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Ozu, Akira; Toh, Yosuke
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(11), p.4002 - 4018, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Morii, Shiori; Yomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 72(10.11), p.441 - 448, 2023/10
Rapid analytical method for the determination of Zr-93 in radioactive wastes has been developed. Laser ablation (LA)-ICP-MS was applied to the analysis of Zr isotopes in simulated high-level radioactive waste (HLW). Sample preparation time was dramatically reduced by using a DGA resin as the adsorbent for Zr. Direct quantification of Zr isotopes in this resin sample was carried out by LA-ICP-MS. Laser settings were optimized to obtain a reliable isotope ratio of the sample by LA-ICP-MS. Quantification of Zr isotopes in the simulated HLW solution by isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) was examined. The amount of Zr-90 in the sample obtained by IDMS corresponded to a value calculated from the given concentration of Zr in the sample within uncertainty. Thus, this method can be applied for the quantification of Zr-93 in radioactive wastes.
Nakamura, Izumi*; Otani, Akihito*; Okuda, Yukihiko; Watakabe, Tomoyoshi; Takito, Kiyotaka; Okuda, Takahiro; Shimazu, Ryuya*; Sakai, Michiya*; Shibutani, Tadahiro*; Shiratori, Masaki*
Dai-10-Kai Kozobutsu No Anzensei, Shinraisei Ni Kansuru Kokunai Shimpojiumu (JCOSSAR2023) Koen Rombunshu (Internet), p.143 - 149, 2023/10
In 2019, the JSME Code Case for seismic design of nuclear power plant piping systems was published. The Code Case provides the strain-based fatigue criteria and detailed inelastic response analysis procedure as an alternative design rule to the current seismic design, which is based on the stress evaluation by elastic response analysis. In 2022, it was approved to revise the Code Case with improving the cycle counting method for fatigue evaluation to the Rain flow method. In addition, the discussion to incorporate the elastic-plastic behavior of support structures is now in progress for the next revision of the Code Case. This paper discusses the contents and background of the 2022 revision, the progress of the next revision, and future tasks.
 B-enriched MgB
B-enriched MgB wire using a pulsed neutron source
wire using a pulsed neutron sourceMachiya, Shutaro*; Osamura, Kozo*; Hishinuma, Yoshimitsu*; Taniguchi, Hiroyasu*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(4), p.34_1 - 34_17, 2023/10
Hironaka, Kota; Lee, J.; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Ito, Fumiaki*; Hori, Junichi*; Terada, Kazushi*; Sano, Tadafumi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1054, p.168467_1 - 168467_5, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)Arai, Yoichi; Watanabe, So; Hasegawa, Kenta; Okamura, Nobuo; Watanabe, Masayuki; Takeda, Keisuke*; Fukumoto, Hiroki*; Ago, Tomohiro*; Hagura, Naoto*; Tsukahara, Takehiko*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 542, p.206 - 213, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)